Introduction to Human Subject Research
Human subject research (HSR) encompasses observational and interventional scientific studies in which human beings serve as the subjects of inquiry following quantitative and qualitative research approaches. Since people are involved in this research, the consistent pursuit of an open science paradigm plays a particularly important role.
Below we briefly describe the general research process in human subject research.
Human Subject Research Process
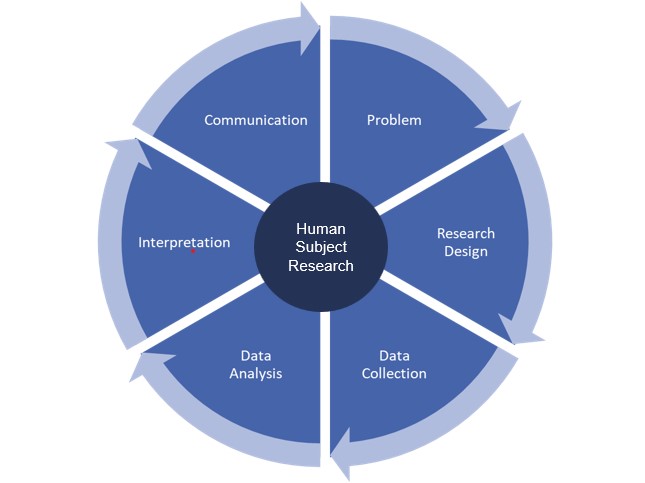
In principle, the human subject research process can be divided into different phases. In our Open Science-based research framework we differentiate between six phases:
- Define Problem: What human behavior or decision do we need to understand?
- Design: Choose method & consider ethics.
- Recruit & Collect: With informed consent.
- Analyze behavior: Patterns, mechanisms, effects.
- Interpret: What do these decisions and behaviors tell us?
- Communicate Findings: Report transparently and responsibly.
Each stage of the human subject process seamlessly leads to the next, and the final stage linking back to the initial problem identification, suggesting that the output of one human subjects research cycle could serve as input to new problems to investigate.